...
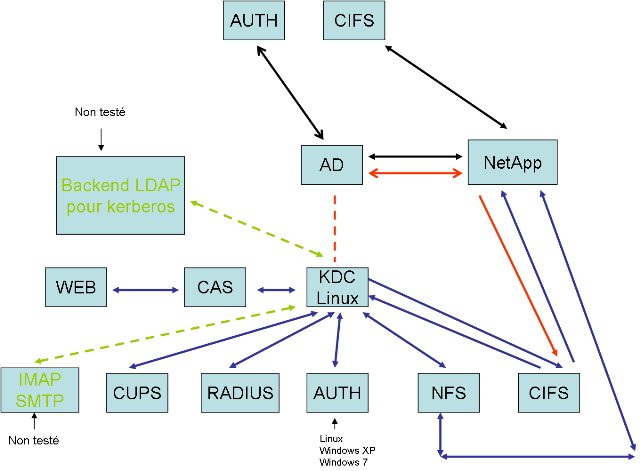
Architecture
Roadmap
Générer les clients Linux, Windows XP et Windows 7.
Mettre en place un serveur Kerberos s'appuyant sur le serveur LDAP.
Valider l'installation en configurant les clients pour qu'ils s'authentifient sur le serveur Kerberos et montent les homedirs des utilisateurs.
Mettre en place un serveur CAS s'appuyant sur le serveur Kerberos, capable de valider les tickets Kerberos des navigateurs des clients.
Valider en testant le SSO depuis les différents clients.
Machines mises en place
Nom | Rôle |
|---|---|
kerb.ifsic.univ-rennes1.fr (148.60.10.50) | Serveur Kerberos |
cas.ifsic.univ-rennes1.fr (148.60.10.51) | Serveur CAS |
clinux.ifsic.univ-rennes1.fr (148.60.10.52) | Client Linux |
cwinxp.ifsic.univ-rennes1.fr (148.60.10.53) | Client Windows XP |
cwin7.ifsic.univ-rennes1.fr (148.60.10.54) | Client Windows 7 |
Installation et configuration des machines
Pour toutes les machines :
- Netmask : 255.255.255.0
- Gateway : 148.60.10.254
- DNS : 148.60.4.1
- NTP : ntp1.univ-rennes1.fr
Serveur Kerberos
Installation système
Boot sur CD Fedora 10.
- FQDN : kerb.ifsic.univ-rennes1.fr
- IP : 148.60.10.50
Packages additionnels installés :
- Servers -> Network servers -> kerb5-server
Configuration NTP
Configuration Kerberos
Modification de quelques fichiers de configuration pour créer le royaume IFSIC.TEST.
/etc/krb5.conf
| Bloc de code |
|---|
[libdefaults]
default_realm = IFSIC.TEST
default_etypes = des3-hmac-sha1 des-cbc-crc
default_tkt_enctypes = des3-hmac-sha1 des-cbc-crc
default_tgs_enctypes = des3-hmac-sha1 des-cbc-crc
permitted_enctypes = des3-hmac-sha1 des-cbc-crc rc4-hmac
|
/var/kerberos/krb5kdc/kdc.conf
| Bloc de code |
|---|
[realms]
IFSIC.TEST = {
#master_key_type = aes256-cts
acl_file = /var/kerberos/krb5kdc/kadm5.acl
dict_file = /usr/share/dict/words
admin_keytab = /var/kerberos/krb5kdc/kadm5.keytab
supported_enctypes = aes256-cts:normal aes128-cts:normal des3-hmac-sha1:normal arcfour-hmac:normal des-hmac-sha1:normal des-cbc-md5:normal des-cbc-crc:normal des-cbc-crc:v4 des-cbc-crc:afs3 rc4-hmac:normal
}
|
/var/kerberos/krb5kdc/kadm5.acl
| Bloc de code |
|---|
*/admin@IFSIC.TEST * |
/etc/gssapi_mech.conf
En 64 bits seulement :
| Bloc de code |
|---|
# library initialization function
# ================================ ==========================
# The MIT K5 gssapi library, use special function for initialization.
libgssapi_krb5.so mechglue_internal_krb5_init |
Création de la base Kerberos :
| Bloc de code |
|---|
[root@kerb ~] kdb5_util create -s |
Ajout du premier utilisateur (root) :
| Bloc de code |
|---|
[root@kerb ~] kadmin.local -q "addprinc root/admin" |
Démarrage des services (auparavant arrêter SeLinux) :
| Bloc de code |
|---|
[root@kerb ~] setenforce 0
[root@kerb ~] chkconfig kadmin on
[root@kerb ~] service kadmin start
[root@kerb ~] chkconfig krb5kdc on
[root@kerb ~] service krb5kdc start |
Vérification en affichant la liste des principals :
| Bloc de code |
|---|
[root@kerb ~]# kadmin
Authenticating as principal root/admin@IFSIC.TEST with password.
Password for root/admin@IFSIC.TEST:
kadmin: listprincs
K/M@IFSIC.TEST
kadmin/admin@IFSIC.TEST
kadmin/changepw@IFSIC.TEST
kadmin/history@IFSIC.TEST
kadmin/kerb.ifsic.univ-rennes1.fr@IFSIC.TEST
krbtgt/IFSIC.TEST@IFSIC.TEST
ldap/zag.ifsic.univ-rennes1.fr@IFSIC.TEST
root/admin@IFSIC.TEST |
Ajout d'un principal pour le KDC lui-même (indispensable pour la réplication) :
| Bloc de code |
|---|
[root@kerb ~]# kadmin
Authenticating as principal root/admin@IFSIC.TEST with password.
Password for root/admin@IFSIC.TEST:
kadmin: addprinc -randkey host/kerb.ifsic.univ-rennes1.fr
WARNING: no policy specified for host/kerb.ifsic.univ-rennes1.fr@IFSIC.TEST; defaulting to no policy
Principal "host/kerb.ifsic.univ-rennes1.fr@IFSIC.TEST" created.
|
Ajout d'un utilisateur (kerb) pour les tests :
| Bloc de code |
|---|
[root@kerb ~]# kadmin
Authenticating as principal root/admin@IFSIC.TEST with password.
Password for root/admin@IFSIC.TEST:
kadmin: addprinc kerb
WARNING: no policy specified for kerb@IFSIC.TEST; defaulting to no policy
Enter password for principal "kerb@IFSIC.TEST":
Re-enter password for principal "kerb@IFSIC.TEST":
Principal "kerb@IFSIC.TEST" created. |
Serveur CAS
Boot sur CD Fedora 10.
- FQDN : cas.ifsic.univ-rennes1.fr
- IP : 148.60.10.51
Serveur LDAP
Il est sur zag.ifsic.univ-rennes1.fr et est appelable en ldaps (certificat auto-signé).
Il contient 2 entrées (dagorn et paubry).
Ci-dessous une entrée :
| Bloc de code |
|---|
ldapsearch -H "ldaps://zag.ifsic.univ-rennes1.fr" -b "dc=univ-rennes1,dc=fr" -x 'uid=dagorn'
# extended LDIF
#
# LDAPv3
# base <dc=univ-rennes1,dc=fr> with scope subtree
# filter: uid=dagorn
# requesting: ALL
#
# dagorn, people, univ-rennes1.fr
dn: uid=dagorn,ou=people,dc=univ-rennes1,dc=fr
loginShell: /bin/bash
employeeNumber: 2848
sn: Francois Dagorn
gidNumber: 1000
objectClass: top
objectClass: inetOrgPerson
objectClass: posixAccount
objectClass: person
objectClass: shadowAccount
objectClass: organizationalPerson
mail: Francois.Dagorn@univ-rennes1.fr
givenName: fd
uid: dagorn
uidNumber: 113
displayName: Francois Dagorn
cn: Francois Dagorn
homeDirectory: /tmp/dagorn
userPassword:: e1NTSEF9TzhBPG95QTlaZDNMckF2Y3k3FG14T0lSb0hES0xYaUs= |
la trace d'un acces sur le port 636 (ldaps) :
| Bloc de code |
|---|
Dec 10 11:36:33 zag slapd[26967]: conn=0 fd=11 ACCEPT from IP=148.60.10.22:43365 (IP=0.0.0.0:636) |
Pour créer ou modifier une entrée, voir dans /tmp/ldap les exemples de fichiers ldif et :
| Bloc de code |
|---|
%ldapmodify -h localhost -D "cn=admin,dc=univ-rennes1,dc=fr" -w "le-mot-de-passe-root-usuel" -x -f test.ldif
%ldapadd -h localhost -D "cn=admin,dc=univ-rennes1,dc=fr" -w "le-mot-de-passe-root-usuel" -x -f test.ldif |
ldap.conf
host zag.ifsic.univ-rennes1.fr
base ou=people,dc=univ-rennes1,dc=fr
URI ldaps://zag.ifsic.univ-rennes1.fr:636/
TLS_REQCERT allow
Client Linux
Boot sur CD Fedora 10.
- FQDN : clinux.ifsic.univ-rennes1.fr
- IP : 148.60.10.52
Client Windows XP
- FQDN : cwinxp.ifsic.univ-rennes1.fr
- IP : 148.60.10.53
Client Windows 7
- FQDN : cwin7.ifsic.univ-rennes1.fr
- IP : 148.60.10.54
Executer cmd.exe en tant qu'administrateur :
...
| Avertissement |
|---|
Les pages ci-dessous montrent une expérience menée à l'IFSIC dans le but de montrer la faisabilité d'une architecture dont l'authentification serait complètement prise en charge par un serveur d'authentification Kerberos. Tous les tests menés ont conclu à la faisabilité, sauf le montage CIFS sur le filer NetApp du CRI, qui nécessite l'appui sur un Active Directory ; les auteurs ont réussi à configurer la relation d'approbation d'un serveur Active Directory vers le serveur Kerberos, mais pas le montage des volumes en CIFS lui-même (à leur grand désespoir...). Deux pistes sont désormais envisagées :
|
Machines mises en place (archive)
Une description de l'architecture mise en place et des acteurs du système.
Installation et configuration du serveur Kerberos (archive)
Comment installer un serveur d'authentification Kerberos.
Intégration d'un client Linux (archive)
Comment intégrer un client Linux dans un royaume Kerberos.
Passage de l'authentification Kerberos aux applications web (mod_auth_kerb)
Comment configurer Apache et mod_auth_kerb pour que l'authentification Kerberos passe du niveau système au niveau applicatif (web).
Installation et configuration du serveur CAS (archive)
Comment installer et configurer un serveur CAS pour qu'il authentifie les utilisateurs par Kerberos et LDAP.
Passage de l'authentification Kerberos à Samba (archive)
Comment mettre en place un serveur Samba et faire passer l'authentification Kerberos des clients lors du montage des volumes.
Passage de l'authentification Kerberos à NFS (v4)
Comment mettre en place un serveur NFS v4 et faire passer l'authentification Kerberos des clients lors du montage des volumes.
CASKERB:802.1X, radius et Kerberos802.1X, radius et Kerberos (archive)
Comment configurer un serveur freeRadius pour qu'il authentifie les usagers sur une base kerberos
Intégration d'un client Windows XP (archive)
Comment intégrer un client Windows XP dans un royaume Kerberos.
Intégration d'un client Windows 7 (archive)
Comment intégrer un client Windows 7 dans un royaume Kerberos.
Problèmes liés au clonage des stations de travail (archive)
Migration de l'authentification de LDAP à Kerberos (archive)
Comment envisager la migration de l'authentification des utilisateurs d'un annuaire LDAP à un serveur Kerberos.
Points restants à voir :
- CUPS et Kerberos
- NetApp et Kerberos
- AD et Kerberos